Monday, October 31, 2011
Wednesday, October 26, 2011
VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION IN OPEN CHANNEL
The measured velocity in an open channel will always vary across the channel section because of friction along the boundary. Neither is this velocity distribution usually axisymmetric (as it is in pipe flow) due to the existence of the free surface. It might be expected to find the maximum velocity at the free surface where the shear force is zero but this is not the case. The maximum velocity is usually found just below the surface. The explanation for this is the presence of secondary currents which are circulating from the boundaries towards the section centre and resistance at the air/water interface. These have been found in both laboratory measurements and 3d numerical simulation of turbulence.
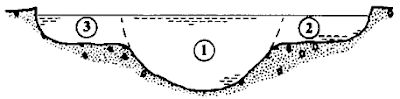
The figure below shows some typical velocity distributions across some channel cross sections. The number indicates percentage of maximum velocity.
Figure of velocity distributions
To determine the values of ? and ? the velocity distribution must have been measured (or be known in some way). In irregular channels where the flow may be divided into distinct regions ? may exceed 2 and should be included in the Bernoulli equation.
The figure below is a typical example of this situation. The channel may be of this shape when a river is in flood – this is known as a compound channel.
Figure of a compound channel with three regions of flow
If the channel is divided as shown into three regions and making the assumption that ? = 1 for each then
Where
The figure below shows some typical velocity distributions across some channel cross sections. The number indicates percentage of maximum velocity.
Figure of velocity distributions
To determine the values of ? and ? the velocity distribution must have been measured (or be known in some way). In irregular channels where the flow may be divided into distinct regions ? may exceed 2 and should be included in the Bernoulli equation.
The figure below is a typical example of this situation. The channel may be of this shape when a river is in flood – this is known as a compound channel.
Figure of a compound channel with three regions of flow
If the channel is divided as shown into three regions and making the assumption that ? = 1 for each then
Where
Saturday, October 15, 2011
How to open MS Office 2007 file in Ms Office 2003
 Hello World!!
Hello World!!Well you may experience with a problem of opening Ms Office 2007 files [.docx, .xlsx,etc] in Ms Office 2003. This happens due to the compatibility difference between these two versions. It is obvious that difference is must between old and new versions. We can fix all these errors by adding the compatibility pack to the Ms Office 2003 which helps to run in low RAM too.
 Download this Compatibility Pack from below servers:
Download this Compatibility Pack from below servers:Monday, September 26, 2011
Saturday, September 17, 2011
ONLINE APPLICATION FOR GATE 2012
GATE 2012
This time the total application procedure of GATE is changed. Everyone should apply in online. Everything is un-editable after once you have submitted your details. So, please fill your details carefully. Read all instructions and FAQ page for clear procedure of application.
The new RULE passed in 2012 that pre-final [3rd year] year students are not eligible to apply GATE 2012.
The new RULE passed in 2012 that pre-final [3rd year] year students are not eligible to apply GATE 2012.
 |
| CLICK IMAGE TO READ THE FAQ PAGE |
 |
| CLICK IMAGE TO APPLY ONLINE |
Wednesday, August 31, 2011
Anna Hazare Jan lokpal bill – Theme song
The Jan Lokpal Bill (Hindi: जन लोकपाल विधेयक), also referred to as the Citizen’s Ombudsman Bill, is a proposed anti-corruption law in India. It was proposed by prominent civil society activists as a more effective improvement to the original Lokpal bill, which is currently being proposed by the the Government of India. The prefix Jan was added to signify the fact that these improvements include input provided by “ordinary citizens” through an activist-driven, non-governmental public consultation.
Drafted by Justice Santosh Hegde (former Supreme Court Judge and former Lokayukta of Karnataka), Prashant Bhushan (Supreme Court Lawyer) and Arvind Kejriwal (RTI activist), the draft Bill to regard a system where a corrupted person found guilty would go to jail within two years of the complaint being made and his ill-gotten wealth being impounded. It also seeks power to the Jan Lokpal Bill to prosecute all politicians and bureaucrats without government permission and intimation.
Drafted by Justice Santosh Hegde (former Supreme Court Judge and former Lokayukta of Karnataka), Prashant Bhushan (Supreme Court Lawyer) and Arvind Kejriwal (RTI activist), the draft Bill to regard a system where a corrupted person found guilty would go to jail within two years of the complaint being made and his ill-gotten wealth being impounded. It also seeks power to the Jan Lokpal Bill to prosecute all politicians and bureaucrats without government permission and intimation.
Wednesday, August 17, 2011
Non-destructive methods for testing Concrete
The standard method of evaluating the quality of concrete in buildings or structures is to test specimens cast simultaneously for compressive, flexural and tensile strengths. The main disadvantages are that results are not obtained immediately; that concrete in specimens may differ from that in the actual structure as a result of different curing and compaction conditions; and that strength properties of a concrete specimen depend on its size and shape.
Although there can be no direct measurement of the strength properties of structural concrete for the simple reason that strength determination involves destructive stresses, several non- destructive methods of assessment have been developed. These depend on the fact that certain physical properties of concrete can be related to strength and can be measured by non-destructive methods. Such properties include hardness, resistance to penetration by projectiles, rebound capacity and ability to transmit ultrasonic pulses and X- and Y-rays. These non-destructive methods may be categorized as penetration tests, rebound tests, pull-out techniques, dynamic tests, radioactive tests, maturity concept. It is the purpose of this Digest to describe these methods briefly, outlining their advantages and disadvantages.
Penetration Tests
Penetration Tests
The Windsor probe is generally considered to be the best means of testing penetration. Equipment consists of a powder-actuated gun or driver, hardened alloy probes, loaded cartridges, a depth gauge for measuring penetration of probes and other related equipment. A probe, diameter 0.25 in. (6.5 mm) and length 3.125 in. (8.0 cm), is driven into the concrete by means of a precision powder charge. Depth of penetration provides an indication of the compressive strength of the concrete. Although calibration charts are provided by the manufacturer, the instrument should be calibrated for type of concrete and type and size of aggregate used.
Limitations and Advantages. The probe test produces quite variable results and should not be expected to give accurate values of concrete strength. It has, however, the potential for providing a quick means of checking quality and maturity of in situ concrete. It also provides a means of assessing strength development with curing. The test is essentially non-destructive, since concrete and structural members can be tested in situ, with only minor patching of holes on exposed faces.
Rebound Tests
The rebound hammer is a surface hardness tester for which an empirical correlation has been established between strength and rebound number. The only known instrument to make use of the rebound principle for concrete testing is the Schmidt hammer, which weighs about 4 lb (1.8 kg) and is suitable for both laboratory and field work. It consists of a spring-controlled hammer mass that slides on a plunger within a tubular housing. The hammer is forced against the surface of the concrete by the spring and the distance of rebound is measured on a scale. The test surface can be horizontal, vertical or at any angle but the instrument must be calibrated in this position.
Calibration can be done with cylinders (6 by 12 in., 15 by 30 cm) of the same cement and aggregate as will be used on the job. The cylinders are capped and firmly held in a compression machine. Several readings are taken, well distributed and reproducible, the average representing the rebound number for the cylinder. This procedure is repeated with several cylinders, after which compressive strengths are obtained.
Limitations and Advantages. The Schmidt hammer provides an inexpensive, simple and quick method of obtaining an indication of concrete strength, but accuracy of ±15 to ±20 per cent is possible only for specimens cast cured and tested under conditions for which calibration curves have been established. The results are affected by factors such as smoothness of surface, size and shape of specimen, moisture condition of the concrete, type of cement and coarse aggregate, and extent of carbonation of surface.
Pull-Out Tests
A pull-out test measures, with a special ram, the force required to pull from the concrete a specially shaped steel rod whose enlarged end has been cast into the concrete to a depth of 3 in. (7.6 cm). The concrete is simultaneously in tension and in shear, but the force required to pull the concrete out can be related to its compressive strength. The pull-out technique can thus measure quantitatively the in-situ strength of concrete when proper correlations have been made. It has been found, over a wide range of strengths, that pull-out strengths have a coefficient of variation comparable to that of compressive strength.
Limitations and Advantages. Although pullout tests do not measure the interior strength of mass concrete, they do give information on the maturity and development of strength of a representative part of it. Such tests have the advantage of measuring quantitatively the strength of concrete in place. Their main disadvantage is that they have to be planned in advance and pull-out assemblies set into the formwork before the concrete is placed. The pull-out, of course, creates some minor damage. The test can be non-destructive, however, if a minimum pull-out force is applied that stops short of failure but makes certain that a minimum strength has been reached. This is information of distinct value in determining when forms can be removed safely.
Dynamic Tests
At present the ultrasonic pulse velocity method is the only one of this type that shows potential for testing concrete strength in situ. It measures the time of travel of an ultrasonic pulse passing through the concrete. The fundamental design features of all commercially available units are very similar, consisting of a pulse generator and a pulse receiver. Pulses are generated by shock-exciting piezo-electric crystals, with similar crystals used in the receiver. The time taken for the pulse to pass through the concrete is measured by electronic measuring circuits.
Pulse velocity tests can be carried out on both laboratory-sized specimens and completed concrete structures, but some factors affect measurement:
- There must be smooth contact with the surface under test; a coupling medium such as a thin film of oil is mandatory.
- It is desirable for path-lengths to be at least 12 in. (30 cm) in order to avoid any errors introduced by heterogeneity.
- It must be recognized that there is an increase in pulse velocity at below-freezing temperature owing to freezing of water; from 5 to 30°C (41 – 86°F) pulse velocities are not temperature dependent.
- The presence of reinforcing steel in concrete has an appreciable effect on pulse velocity. It is therefore desirable and often mandatory to choose pulse paths that avoid the influence of reinforcing steel or to make corrections if steel is in the pulse path.
Applications and Limitations: The pulse velocity method is an ideal tool for establishing whether concrete is uniform. It can be used on both existing structures and those under construction. Usually, if large differences in pulse velocity are found within a structure for no apparent reason, there is strong reason to presume that defective or deteriorated concrete is present.
High pulse velocity readings are generally indicative of good quality concrete. A general relation between concrete quality and pulse velocity is given in Table.
General Conditions Pulse Velocity ft/sec
Excellent Above 15,000
Good 12,000-15,000
Questionable 10,000-12,000
Poor 7,000-10,000
Very Poor below 7,000
Fairly good correlation can be obtained between cube compressive strength and pulse velocity. These relations enable the strength of structural concrete to be predicted within ±20 per cent, provided the types of aggregate and mix proportions are constant.
The pulse velocity method has been used to study the effects on concrete of freeze-thaw action, sulphate attack, and acidic waters. Generally, the degree of damage is related to a reduction in pulse velocity. Cracks can also be detected. Great care should be exercised, however, in using pulse velocity measurements for these purposes since it is often difficult to interpret results. Sometimes the pulse does not travel through the damaged portion of the concrete.
The pulse velocity method can also be used to estimate the rate of hardening and strength development of concrete in the early stages to determine when to remove formwork. Holes have to be cut in the formwork so that transducers can be in direct contact with the concrete surface. As concrete ages, the rate of increase of pulse velocity slows down much more rapidly than the rate of development of strength, so that beyond a strength of 2,000 to 3,000 psi (13.6 to 20.4 MPa) accuracy in determining strength is less than ±20%. Accuracy depends on careful calibration and use of the same concrete mix proportions and aggregate in the test samples used for calibration as in the structure.
In summary, ultrasonic pulse velocity tests have a great potential for concrete control, particularly for establishing uniformity and detecting cracks or defects. Its use for predicting strength is much more limited, owing to the large number of variables affecting the relation between strength and pulse velocity.
Radioactive Methods
Radioactive methods of testing concrete can be used to detect the location of reinforcement, measure density and perhaps establish whether honeycombing has occurred in structural concrete units. Gamma radiography is increasingly accepted in England and Europe. The equipment is quite simple and running costs are small, although the initial price can be high. Concrete up to 18 in. (45 cm) thick can be examined without difficulty.
Saturday, August 13, 2011
Averting Bridge Disasters: New Technology Could Save Hundreds of Lives
- Millions of U.S. drivers cross faulty or obsolete bridges every day, highway statistics show, but it's too costly to fix all these spans or adequately monitor their safety, says a University of Maryland researcher who's developed a new, affordable early warning system.
This wireless technology could avert the kind of bridge collapse that killed 13 and injured 145 along Minneapolis' I-35W on Aug. 1, 2007.
"Potentially hundreds of lives could be saved," says University of Maryland electrical engineering researcher Mehdi Kalantari. "One of every four U.S. highway bridges has known structural problems or exceeded its intended life-span. Most only get inspected once every one or two years. That's a bad mix." Kalantari has created tiny wireless sensors that monitor and transmit minute-by-minute data on a bridge's structural integrity. A central computer analyzes the data and instantly warns officials of possible trouble. He plans to scale-up manufacture in the fall.
"If this kind of technology had been available in Minnesota four years ago, there's a good chance the fatal bridge collapse could have been avoided," Kalantari adds. "This new approach makes preventive maintenance affordable -- even at a time when budgets are tight. Officials will be able to catch problems early and will have weeks or month to fix a problem."
More than one-in-four U.S. bridges are either structurally deficient or functionally obsolete, according to a 2009 estimate by the U.S. Society of Civil Engineers.
- 72,000-plus U.S. bridges are listed by the U.S. Department of Transportation as "structurally deficient" and require extra surveillance.
- 79,000 others are functionally obsolete, exceeding their life-span and carrying loads greater than they were designed to handle.
Kalantari's sensors measure indicators of a bridge's structural health, such as strain, vibration, flexibility, and development of metal cracks. The sensors are small, wireless, rugged, and require practically no maintenance, he says. They are expected to last more than a decade, with each costing about $20. An average-sized highway bridge would need about 500 sensors for a total cost of about $10,000.
"The immediacy, low cost, low energy and compact size add up to a revolution in bridge safety monitoring, providing a heightened level of early-warning capability," Kalantari concludes.
Newer "smart" bridges, including the I-35W replacement in Minneapolis, have embedded wired networks of sensors. But Kalantari says the cost is too high for use on older spans.
"A wired network approach will cost at least 100 times more than a wireless alternative, and that's simply unaffordable given the strain on local, state, and federal budgets," Kalantari estimates.
Current federal requirements call for an on-site, visual inspection of highway bridges once every two to five years, depending the span's condition. Bridges deemed structurally deficient must be inspected once each year.
In its report on the fatal Minneapolis bridge collapse, the National Transportation Safety Board identified a faulty "gusset plate" -- a connector essential to the bridge's structural integrity -- as a likely cause of the disaster.
The report notes an "inadequate use of technologies for accurately assessing the condition of gusset plates on deck truss bridges." Kalantari expects his technology to fill that need.
Testing of Maryland bridges
For almost a year, Kalantari has been testing his device in conjunction with the Maryland Department of Transportation, measuring the structural parameters of highway bridges in a real setting. This has enabled him to optimize the device's performance and energy consumption. His updated model is smaller and ten times more energy efficient than its predecessor.
The testing allows him to track the bridge's response to changes in weather conditions and traffic. For example, he's measuring how the metal expands and contracts as the temperature rises and falls. Also, he can compare the metal's response during periods of peak and light loads. He hopes to expand the field testing more broadly in Maryland and to deploy sensors fully across the spans.
- Capital Beltway (I-495), Northwest Branch Bridge: Since August 2010, Kalantari has had eight sensors on the Northwest Branch Bridge, a truss span like the one that collapsed in Minneapolis, though smaller. The bridge has proven "safe" in all his tests, so far. "Everything is working the way it's supposed to -- both the bridge and my instruments," he reports.
- Frederick, Maryland (I-70), Conococheague Creek Bridge: This span is the second provided by Maryland highway officials for Kalantari's test.
How the system works
As with conventional technology, the sensors measure variables reflecting the structural integrity of a bridge, such as strain, vibration, tilt, acceleration, deformation and cracking.
Serious problems are more obvious and easier to interpret, and so trip an alarm very quickly. Early-stage problems are more subtle, and it may take up to a few days until the system is confident enough to report a structural integrity issue.
The sensors are less than five millimeters thick and have four thin, flexible layers. The first senses and measures structural parameters; the second stores energy; the third communicates data; and the outer layer harvests energy from ambient light and ambient radio waves.
Kalantari says the sensors offer a significant improvement on existing technology:
- No wires, batteries, or dedicated external power source.
- Almost no maintenance
- Low cost
- Easy and quick to install
- Suitable for new and existing bridges.
Story Source:
Friday, July 8, 2011
How to prepare for GATE ?
GATE preparing can be easy as preparing for your University Exams. The main thing is you should start early with a quality books [i mean with good subject] and guidance. The main thing is you must remember that GATE paper focus on your in depth knowledge of subject, your basics, presence of mind during examination etc.
Following are the recommendations while preparing for your GATE exams:
The questions are generally derivations of the fundamentals. First get your fundamentals right, and then test yourself on those fundamentals. When you have done this, you should pit yourself with the competition, which means a mock test which would give you a percentile to let you know where you stand amongst competitors. How do you choose which coaching material to go with. This is something that is quite subjective. A coaching material cannot be assessed until you have gone through it. So, you could go by the word of your seniors[i mean both senior students and your Professors too] as to what coaching material they followed to prepare for GATE. Here are some parameters on which you can decide whether you should go for a particular coaching institute, use a particular coaching material, or tests:
1. Material Collection
- Syllabus: First collect the syllabus from official site. CLICK HERE to view the syllabus.
- Divide the books in two groups - Fundamental and basic concepts & Problem oriented
- Some good guide books for GATE
- Previous questions papers
3. Start from the basics:
- Refer at least 5 books, it will widen your knowledge.
- Note down the probable concepts (definitions, unit, dimension etc.)
- Note down necessary theories, formulae etc
- Solve problems as maximum as possible (from text books, Guide books etc)
- Think about various tricks in solving problems(if necessary, note it)
- Go for series of self tests based on this chapter(take other’s help to conduct tests)
- Continue the self tests until getting a very good score
5. Follow the same procedure for the rest chapters
6. Finally, go for self tests based on whole syllabus (take other’s help to conduct these tests)
WHEN SHOULD I START PREPARATION FOR GATE?
Seniors recommend to start your GATE preparations right from the second year of your engineering. Buy good books and study materials for GATE. Collect previous Question Papers, Mock test papers and solve them. This not only helps to excel in your University Exams, but also help you to grasp fast and digesting the concepts. The main thing you should revise always else, every effort become worthless with out revising and self check.
HOW GATE IS HELPFUL FOR RESEARCH?
Admission to post graduate programmes with MHRD and some other government scholarship/assistantship at engineering colleges/institutes in the country are open to those who qualify through GATE. GATE qualified candidates with Bachelor degree in Engineering/ Technology/ Architecture/ Pharmacy or Master degree in any branch of Science/Mathematics/Statistics/Computer Applications are eligible for Master/Doctoral programmes in Engineering/ Technology/Architecture/Pharmacy as well as for Doctoral programmes in relevant branches of Science. Some institutions specify GATE as the mandatory qualification even for admission of self-financing students to postgraduate programmes. GATE qualified candidates in Engineering disciplines are also eligible for the award of Junior Research Fellowship in CSIR Laboratories. Some government organizations prescribe GATE qualification as a requirement for applying to the post of a Scientist/Engineer. |
| Click Image to Download the GATE 2011- Question Paper |
 |
| Click Image to Download the GATE 2011- Key |
For any other information, kindly leave a comment, we will try to reply to your queries.
Types of Admixtures for Concrete
 |
| Admixtures |
Admixtures are ingredients other than aggregates, water, fibers, and hydraulic cement that are added to the concrete batch immediately before or during mixing. A proper use of admixtures offers some particular beneficial effects to concrete, improved quality, acceleration or retardation of setting time, increases frost and sulfate resistance, control of strength development, and improved workability.
Calcium chloride (CaCl_2)
Calcium chloride is generally used in cold weather to accelerate the setting time and produces an early finish of the concrete. CaCl_2 can effect the characteristics of concrete causing corrosion of unprotected reinforcement, in a decrease the resistance to freeze, increased internal stresses, an increase in the attack of sulfates, temperature rise, and an increase in the amount of drying shrinkage between 10 - 50 %.
Set Retarding Agents
These agents are primarily used for delaying the setting time of concrete. Set retards are useful, but are not the solution to poorly designed mixes. These retarders must be uniformly dispersed throughout the whole mix [mortar] . Failure to do so will result in the admixture remaining in voids and causing some areas to remain plastic. This leads to plastic shrinkage.
Water Reducing Agents
A certain amount of the water is added to concrete to make the concrete place able and to ignite the hydration reaction of Portland cement. Over 50% of the water have no useful effect and have direct results in durability, the strength of concrete and drying shrinkage. These water reducing agents added to the concrete reduce the water demands of the mix, increase the strength, to reduce the cost, maintain the workability, reduce segregation, reduce honeycombing, reduce cracking, reduce bleeding, and permeability, increase bond strength of concrete to steel, and reduce drying shrinkage. An average of 12 to 15 % reduction in the total water content will accomplish this goal.
Accelerating Agents
These Accelerating agents are used to shorten the setting time and increase the early strength of the concrete. These agents are mainly used for concrete needing to be used immediately in some special cases like the marine constructions etc.
Air Entraining Agents
These Air entraining agents are used primarily to increase the resistance of freezing and thawing. They also produce
- lower water demands for a particular slump,
- high resistance to deicing chemicals,
- to improve workability,
- reduce segregation and bleeding,
- increase durability, and improve pump ability and
- reduce the amount of fine aggregate needs in the mixture.
Even though air entrainments have no effect on drying shrinkage, they create a slight deficit in the concrete strength.
Monday, July 4, 2011
Technozion - NIT Warangal
Technozion is back with more than a bang. With Technozion X bringing home the X factor, They bring to you the X and more! With this year’s theme centering on technology and evolution, they have brought to the table quite a few changes with more events and guest lectures than ever before. Online events and spotlight events, workshops for those who want to learn, and for those who want to share their knowledge. Three days lined up with Robotics and many more events ready to set Warangal sizzling in the cool autumn.
Special Focus on CIVIL ENGINEERING events:
- CONCRETE CANOE
Science behind the Concrete Canoe:
Principle:
Ignoring hydrodynamic effects, all ships or boats float because the weight of the water they displace is equal to the weight of the boat (Archimedes' principle). However, many boats are made of materials that are denser than water, meaning that the boat will sink if filled with water. Although it is not required by the rules of the competition, some competitive concrete canoes have concrete mix designs that are less dense than water. They must pass a test in which the canoe is filled with water and pushed below the surface; the canoe must then resurface in order to qualify for racing. This is possible because, unlike normal concrete which uses sand and small rocks, concrete canoes are created with porous aggregates such as Macrolite and microspheres. However, because many teams still design their concrete mixes to be denser than water, in the United States, teams are allowed to insert concrete-covered, non-structural foam pieces in their canoes to make the canoes float after being submerged.
- TENSIGRITY
He who is afraid to experiment will never see the path of progress . A bold experiment which has grown into a hotspot for civil engineers and almost anyone who has ever admired the beauty of any structure . This innovative event requires participants to build structures with multiple struts or beams which do not touch each other and are supported just by strings !
For more details: TECHNOZION
For more details: TECHNOZION
Friday, April 22, 2011
Important info for 2011 Pass outs of JNTU-HYD , JNTU-KAKINADA & JNTU-ANANTAPUR
We had started this posting in order to clarify few doubts that are in the minds of 4-2 (R07) students of B.Tech/B.Pharmacy. Go through the each & every points that are given below & if u still have any more doubts just reply here so that we will try to help u out.
Note : This posting is common for 4-2 (R07) ==> JNTU-HYD , JNTU-KAKINADA & JNTU-ANANTAPUR students.
Results
Results will be declared within 15 to 20 days after all the branches exams are completed.
Certificates that will be issued after 4-2 Results
After declaring the results JNTU will issue 4-2 indiviual memo, CMM, PC & OD.
CMM: Consolidated Marks Memo/credit sheet (which contains marks of all years)
CLICK HERE FOR SAMPLE CMM
PC: Provisional Certificate
Sample PC screenshot is available in the below link. image is re-sized , Just click on it for the orginal resolution.
CLICK HERE FOR SAMPLE PC
OD: Orginal Degree (That will be issued only after the convocation).
Note:CMM,PC & 4-2 Memo will be issued within one week after declaring the results. You can collect them from your respective colleges.
Info on Advance Supplies
Advance Supplies will be conducted only for 4-2 Semester Subjects.
The advance supplies will be conducted in selected colleges only (i.e., u need to write the exams only in colleges [centres] that will be issued by JNTU)
===============================================================================
Questions asked by many R07 regulation students.
What is the requirement to get the degree For R07 B.Tech Students?
As per B.Tech (R07) regulations, one of the academic requirement to award degree is that the student should secure 216 credits (out of 224 credits registered) with the compulsory subjects as listed below:
1. All the first year subjects
2. All the practical subjects
3. Industry oriented mini-project
4. Seminar
5. Project works.
Can R07 B.Tech students leave 2 subjects & get the degree ?
Yes according to the academic regulations of B.Tech R07 , students can leave any 2 subjects From 2,3,4 years (subjects which have 4 credits) & get the degree.
Can B.Tech R07 Lateral Entry Students leave 2 subjects under the exception of 2 subjects ?
Yes they can.
Can i leave the 1/2 subjects now itself & apply for the undertaking form ?
You can apply only after respective JNTU regions releases the notification on the exception of 2 subjects rule.
What Does Practical subjects mean ?
Practical subjects are Labs in each semester.
Can we leave lab based subjects (Theory subjects) ?
Yes one can leave lab based subjects as exception of 2 subjects.
Example : If a student of R07 regulation has a backlog in MICRO PROCESSOR Theory subject then he can leave that subject. But he can't leave the Micro Processor Lab.
Can i leave 1st Year subjects ?
No , according to the R07 academic regulations u can't leave any 1st year subjects as of now.
Does JNTU mention any FAIL or Star Mark in the certificates if i leave 1/2 subjects as exception of 2 subjects ?
For JNTU-HYD students In the PC,CMM there will not be any indication of Fail. But on the concerned semester marks memo "Fail" will be indicated. But star mark will be given for those 1/2 subjects in which u had failed.
For JNTU-KAKINADA students In the PC there will not be any indication of Fail. But on the concerned semester marks memo "Fail" will be indicated and also on Consolidated Marks Memo (CMM) "Fail" will appear for those one/two subjects.
Note: Star Mark(*) indicates that those 2 subjects marks are excluded while calculating the total %.
If i clear all the subjects & secure 224 credits will i get any star mark in my CMM?
yes u will get the star mark in the subjects (From 2,3,4 Years) in which u secured lease marks. Star Mark indicates that those 2 subjects marks are excluded while calculating the %. A sample CMM can be seen total % , You can see a sample CMM from the below link.
CLICK HERE FOR SAMPLE CMM
What is the Difference between the JNTU-HYD students 216 credits & 224 credits?
For the students who secures 216 credits (failed/leaving 2 subjects) they will exclude those 2 subjects in which he failed while calculating total %. where as for the students who secured 224 credits JNTU will exclude 2 subjects from 2,3,4 Years in which he/she secured least marks.
What happens if i fail & leave those one/two subjects. Does it effect my carrier ?
- Many of the companies recruits only the students who does not have any active backlogs/arrears.
- Suppose a CSE student fails in Operating Systems and Computer Organization courses and applies for a PC, this may affect in getting a job An ECE student who failed in VLSI and DSP subjects may not get admission in M.Tech. in VLSI/DSP specializations.Similarly for other branch students.
- If a candidate is in urgency to submit the PC for Visa, for higher studies then he/she may apply for PC even they acquire 216 or 220 credits, because that may not affect them.
- Therefore if there is no urgent requirement for PC, it is better, the students pass all the subjects and take PC. The students have the option to apply for PC at any time if it is required. They have to apply through 'Tatkal' if they require it immediately.
Do i need to apply for the CMM , PC after declaring the results ?
JNTU-HYD students (if at all u secured 224 credits) then u no need to apply for CMM,PC. You can get the CMM,PC directly from your respective colleges within 1 or 2 weeks after declaring the results.
JNTU-KAKINADA & JNTU-ANANTAPUR students need to apply for the CMM,PC in the prescribed format which is given by the respective university. Taktal process is also avaliable if u r in a urgent need of CMM,PC . Through Tatkal process u can get them wihtin 2 days.
Do i need to apply for CMM,PC if i secure 216 credits out of 224 credits (i.e., if u leave 1/2 subjects)?
JNTU-HYD students need to fill the undertaking form (stating that they wont appear for any further supplies exams for those 1/2 subjects) & submit it in the college exam branch. they will get the CMM,PC with in 2 weeks after doing the above process.
JNTU-KAKINADA & JNTU-ANANTAPUR can apply in the process stated by the university (University will mention it by releasing a notification after declaring the results).
I had applied for the CMM,PC by filling the undertaking form, can i attend for supple exams ?
No u can't attend for the supple exams of those subjects that u had applied in the exception of 2 subjects rule.
I had given my supple for 1/2 exams & before the results are declared i had applied for the CMM,PC by filling the undertaking form. Does i get my result now?
u will not get the results Once if u apply for the CMM,PC under the exception of 2 subjects rule.
can i get my PC,CMM after clearing all the subjects (i.e., securing 224 credits) ?
Yes at a time after u secure 224 credits u can get the CMM & PC.
Rules for Award of Class
Note:
- Pharmacy students need to secure 224 credits to get the degree.
- All the above information is collected from different exam branches & given according to my best knowledge. Do verify with your respective college exam branches/exam cell before u proceed further.
- All the requests to the university should be forwarded through college principal only.
- if any other website copy the above posted content do mention source as www.civlizers.tk
- If u still have any more quires do reply to the posting we will try to clarify them by giving the best possible solution.
A list of Mini / Final Project topics
- Rehabilitation and Resettlement Policy
- Concrete Technology
- Water Resources Engineering
- Eco-concrete Opportunities and Challenges
- Air Pollution Control
- Engineering Behavior Of Soils And Foundations
- Global Positioning And Geographical Information Systems Applications
- Highway Design
- Zfs
- Instrumentation and sensing technology
- Remote Sensing , GIS And Its Applications
- Application of Genetic Algorithm in Irrigation Scheduling
- Geo-technical Engineering
- Water Resources Engineering
- Actuator systems based on Piezoelectric ceramics
- Structural Engineering
- Building Planning and Design
- Recent trends in electricity pricing
- Grid stability using non-conventional energy sources
- Repair Using Modern Materials & Techniques
- Laminated Floorings
- Advance Construction Techniques
- Mixed Traffic Control & Behavior
- Continuously Reinforced Concrete Pavement
- Formwork and supportive scaffolding
- Global Positioning System
- Marine Pollution
- Advances in composite materials
- Reflection Cracking Of Bituminous Overlay and Its Control
- Bamboo as a Building Material
- Construction Engineering Systems
- Advance Construction Techniques
- Power quality improvement
- Soil And Water Conservation / Watershed management
- Hydraulic Structure And Water Power Engg.
- Highway Safety
- Piano Key Spillways for Dams
- Structural Behavior Measurement
- Geo technical Engineering
- Water Resources Development in Developing Countries
- Bio ? Engineering Techniques For Erosion Control In Slope
- Construction Challenges For Bridges In Hilly Area
- Natural Fibres In Concrete
- Fatigue Behaviour Of Steel Fibre Reinforced Concrete Beams
- Continuously Reinforced Concrete Pavement
- Mineral Admixtures For High Performance Concrete
- Restoration Of Monuments
- Construction Safety Management
- Seismic Isolation Devices
- Use Of Polymer Composites In Bridge Rehabilitation
- Impact Of Lightining On Building And Its Remedial Measures
- Modern Concepts Of Rural Road Development
- Pavement Evaluation And Application Of Geotextiles In Pavements
- Design Considerations For Roadside Safety
- Emergency Shelter Through Superadobe Technology
- Production of Biogas From Paddy Straw
- Reactive Powder Concrete
- Bio-medical waste management and the strategy
- Provision of Tunnels
- Construction Safety Management
- Decorative concretes
- GIS and Its Applications
- Rehabilitation Of Buildings and Bridges
- Remote Sensing
- Seismic Analysis Of Structures (Bridges)
- Liquefaction Potential Assessment
- The Role Of Soils In Purifying Wastewater Effluents
- Natural Fibres In Concrete
- Soil Stabilization With Rice Husk Ash and Lime Sludge
- Thermally Comfortable Passive House For Tropical Uplands
- Water Supply and Sanitation
- Environmental Impact Assessment
- Formwork Types & Design
- Disaster Recovery
- Value Engineering
- Trenchless Technology
- Space Hotel
- Green Buildings For Quality Living
- Recycled Aggregate Concrete
- Flexible Pavement
- Repair And Strengthening Of Concrete Structure
Friday, March 25, 2011
PREVIOUS QUESTION PAPERS
JNTU HYD 3-2 External question papers are here for free to download. Please check on FORUM page or
Click here for direct download








 8:28 AM
8:28 AM
 CIVIL-CATS
CIVIL-CATS






 Posted in:
Posted in: 















